SECTION II (Continued)
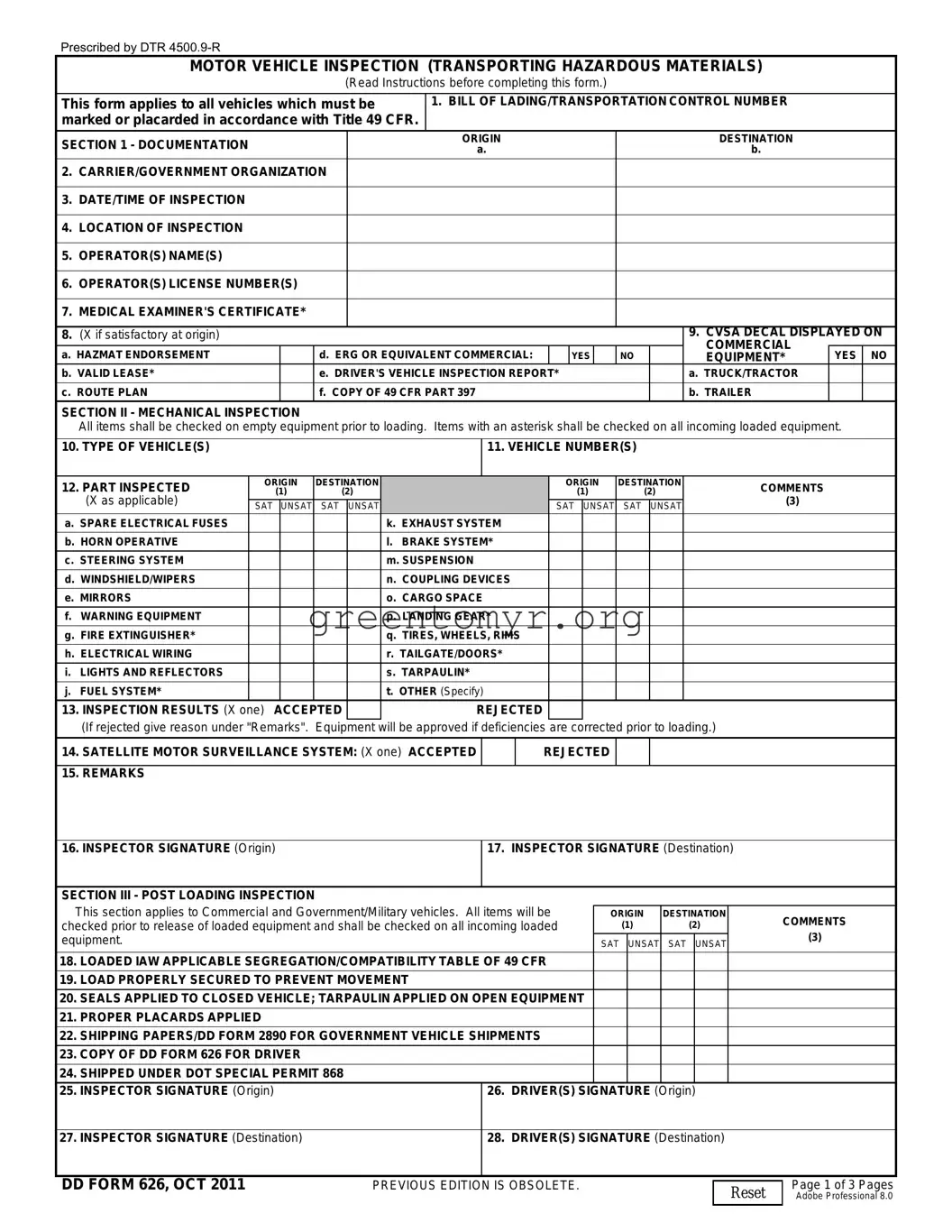
i.Lights/Reflectors. (Head, tail, turn signal, brake, clearance, marker and identification lights, Emergency Flashers). Inspect to see that all lighting devices and reflectors required are operable, of proper color and properly mounted. Ensure that lights and reflectors are not obscured by dirt or grease or have broken lenses. High/Low beam switch must be operative. Emergency Flashers must be operative on both the front and rear of vehicle. (49 CFR 393.24, 25, and 26)
j.Fuel System. Inspect fuel tank and lines to ensure that they are in serviceable condition, free from leaks, or evidence of leakage and securely mounted. Ensure that fuel tank filler cap is not missing. Examine cap for defective gasket or plugged vent. Inspect filler necks to see that they are in completely serviceable condition and not leaking at joints. (49 CFR 393.83)
k.Exhaust System. Exhaust system shall discharge to the atmosphere at a location to the rear of the cab or if the exhaust projects above the cab, at a location near the rear of the cab.
Exhaust system shall not be leaking at a point forward of or directly below the driver compartment. No part of the exhaust system shall be located where it will burn, char or damage electrical wiring, fuel system or any other part of the vehicle. No part of the exhaust system shall be temporarily repaired with wrap or patches. (49 CFR 393.83)
l.Brake System (to include hand brakes, parking brakes and Low Air Warning devices). Check to ensure that brakes are operational and properly adjusted. Check for audible air leaks around air brake components and air lines. Check for fluid leaks, cracked or damaged lines in hydraulic brake systems. Ensure that parking brake is operational and properly adjusted. Low Air Warning devices must be operative. (49 CFR 393.40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, and 55)
m.Suspension. Inspect for indications of misaligned, shifted or cracked springs, loosened shackles, missing bolts, spring hangers unsecured at frame and cracked or loose U-bolts. Inspect for any unsecured axle positioning parts, and sign of axle misalignment, broken torsion bar springs (if so equipped). (49 CFR 393.207)
n.Coupling Devices (Inspect without uncoupling). Fifth Wheels: Inspect for unsecured mounting to frame or any missing or damaged parts. Inspect for any visible space between upper and lower fifth wheel plates. Ensure that the locking jaws are around the shank and not the head of the kingpin. Ensure that the release lever is seated properly and safety latch is engaged. Pintle Hook, Drawbar, Towbar Eye and Tongue and Safety Devices: Inspect for unsecured mounting, cracks, missing or ineffective fasteners (welded repairs to pintle hook is prohibited). Ensure safety devices (chains, hooks, cables) are in serviceable condition and properly attached. (49 CFR 393.70 and 71)
o.Cargo Space. Inspect to ensure that cargo space is clean and free from exposed bolts, nuts, screws, nails or inwardly projecting parts that could damage the lading. Check floor to ensure it is tight and free from holes. Floor shall not be permeated with oil or other substances. (49 CFR 393.84)
p.Landing Gear. Inspect to ensure that landing gear and assembly are in serviceable condition, correctly assembled, adequately lubricated and properly mounted.
SECTION II (Continued)
q.Tires, Wheels and Rims: Inspect to ensure that tires are properly inflated. Flat or leaking tires are unacceptable. Inspect tires for cuts, bruises, breaks and blisters. Tires with cuts that extend into the cord body are unacceptable. Thread depth shall not be less than: 4/32 inches for tires on a steering axle of a power unit, and 2/32 inches for all other tires. Mixing bias and radial on the steering axle is prohibited. Inspect wheels and rims for cracks, unseated locking rings, broken, loose, damaged or missing lug nuts or elongated stud holes. (49 CFR 393.75)
r.Tailgate/Doors. Inspect to see that all hinges are tight in body. Check for broken latches and safety chains. Doors must close securely. (49 CFR 177.835(h))
s.Tarpaulin. If shipment is made on open equipment, ensure that lading is properly covered with fire and water resistant tarpaulin. (49 CFR 177.835(h))
t.Other Unsatisfactory Condition. Note any other condition which would prohibit the vehicle from being loaded with hazardous materials.
Item 14. For AA&E and other shipments requiring satellite surveillance, ensure that the Satellite Motor Surveillance System is operable. The DTTS Message Display Unit, when operative, will display the signal "DTTS ON". The munitions carrier driver, when practical, will position the DTTS message display unit in a manner that allows the shipping inspector or other designated shipping personnel to observe the "DTTS ON" message without climbing aboard the cab of the motor vehicle.
SECTION III - POST LOADING INSPECTION
General Instructions.
All placarded quantities items will be checked prior to the release of loaded equipment. Shipment will not be released until deficiencies are corrected. All items will be checked on incoming loaded equipment. De- ficiencies will be reported in accordance with applicable service regulations.
Item 18. Check to ensure shipment is loaded in accordance with 49 CFR Part 177.848 and the applicable Segregation or Compatibility Table of 49 CFR 177.848.
Item 19. Check to ensure the load is secured from movement in accordance with applicable service outload drawings.
Item 20. Check to ensure seal(s) have been applied to closed equipment; fire and water resistant tarpaulin applied on open equipment.
Item 21. Check to ensure each transport vehicle has been properly placarded in accordance with 49 CFR 172.504.
Item 22. Check to ensure operator has been provided shipping papers that comply with 49 CFR 172.201 and 202. For shipments transported by Government vehicle, shipping paper will be DD Form 2890.
Item 23. Ensure operator(s) sign DD Form 626, are given a copy and understand the hazards associated with the shipment.
Item 24. Applies to Commercial Shipments Only. If shipment is made under DOT Special Permit 868, ensure that shipping papers are properly annotated and copy of Special Permit 868 is with shipping papers.
Item 26. Ensure driver/operator signs DD Form 626 at origin.
Item 28. Ensure driver/operator signs DD Form 626 at destination.