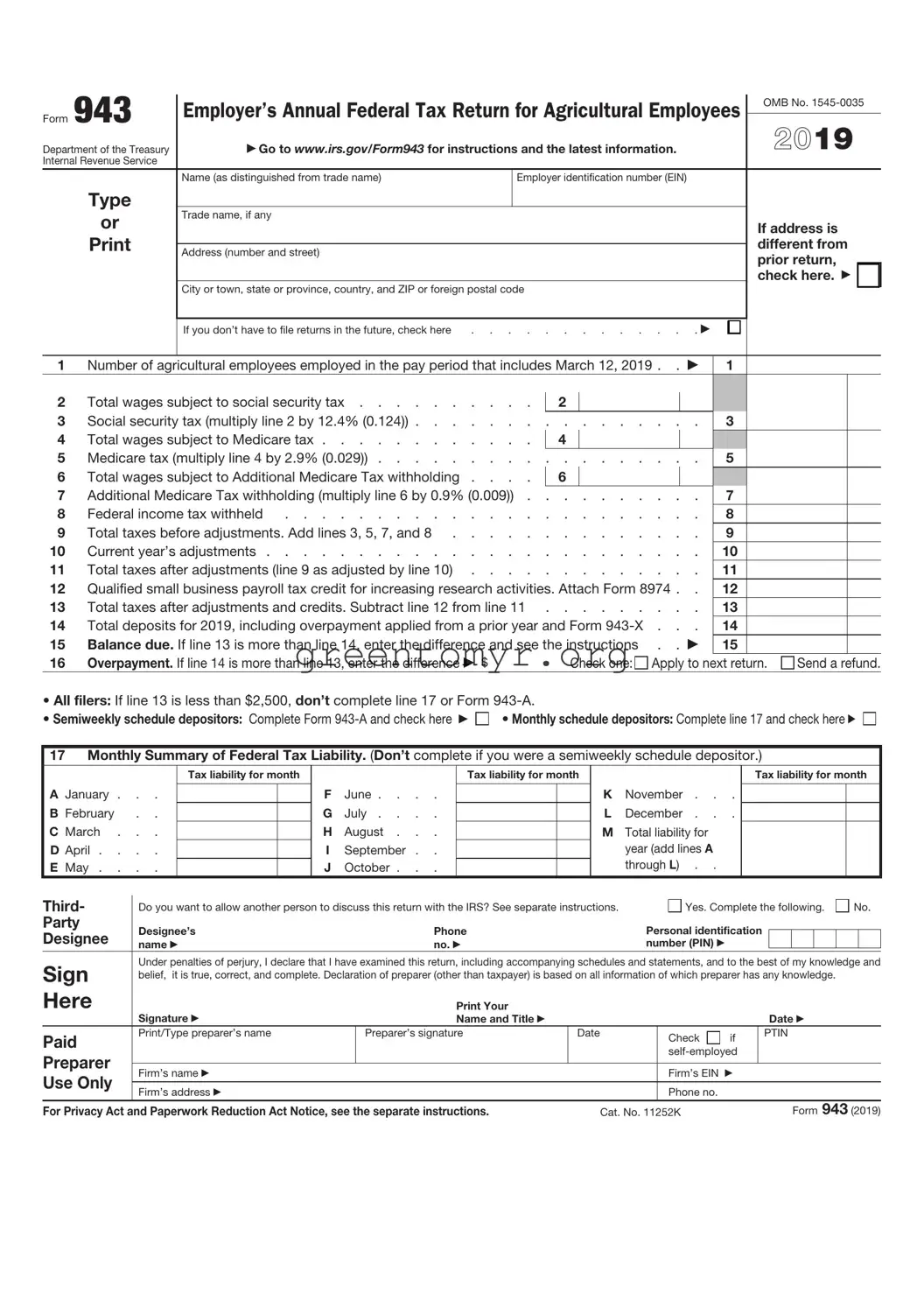
Filling out the IRS 943 form can be challenging. Many people trip over common mistakes that can lead to complications down the line. One frequent error occurs with the employer’s identification number (EIN). Failing to enter the correct EIN not only causes delays but can also result in penalties. Always double-check this critical piece of information.
Another mistake is neglecting to report all wages. If someone forgets to include specific wages paid to seasonal farmworkers, it can lead to inaccuracies in tax calculations. Every bit of information is essential. Ensure all figures are accounted for completely.
People often miss the deadlines for submission. The IRS has strict timelines, and submitting the form late incurs penalties. Mark your calendar well in advance. This proactive measure helps avoid last-minute rushes or forgetfulness.
Using incorrect codes for occupational classifications is a common issue as well. These codes help in determining tax obligations for different types of farm work. Using the wrong code can lead to tax miscalculations that may require additional forms of correction later.
Many also underestimate the importance of signing the form. A signature is critical for validating the information provided. Omitting this could postpone processing and lead to challenges you don’t want to deal with.
Another common blunder is overlooking the importance of reviewing the entire form before submission. Taking the time to go over everything before sending can reveal simple mistakes or oversights that, if left uncorrected, could cause significant problems.
Failure to include all necessary attachments is another area of concern. Some people forget that certain documents must accompany the IRS 943 form. Ensure you are familiar with all requirements and gather the necessary paperwork to avoid this issue.
Lastly, not seeking professional help when needed can be a significant mistake. Tax laws can be complicated. If you’re unsure about certain aspects, consider consulting with a tax professional. Taking this step can save you time and money in the long run.