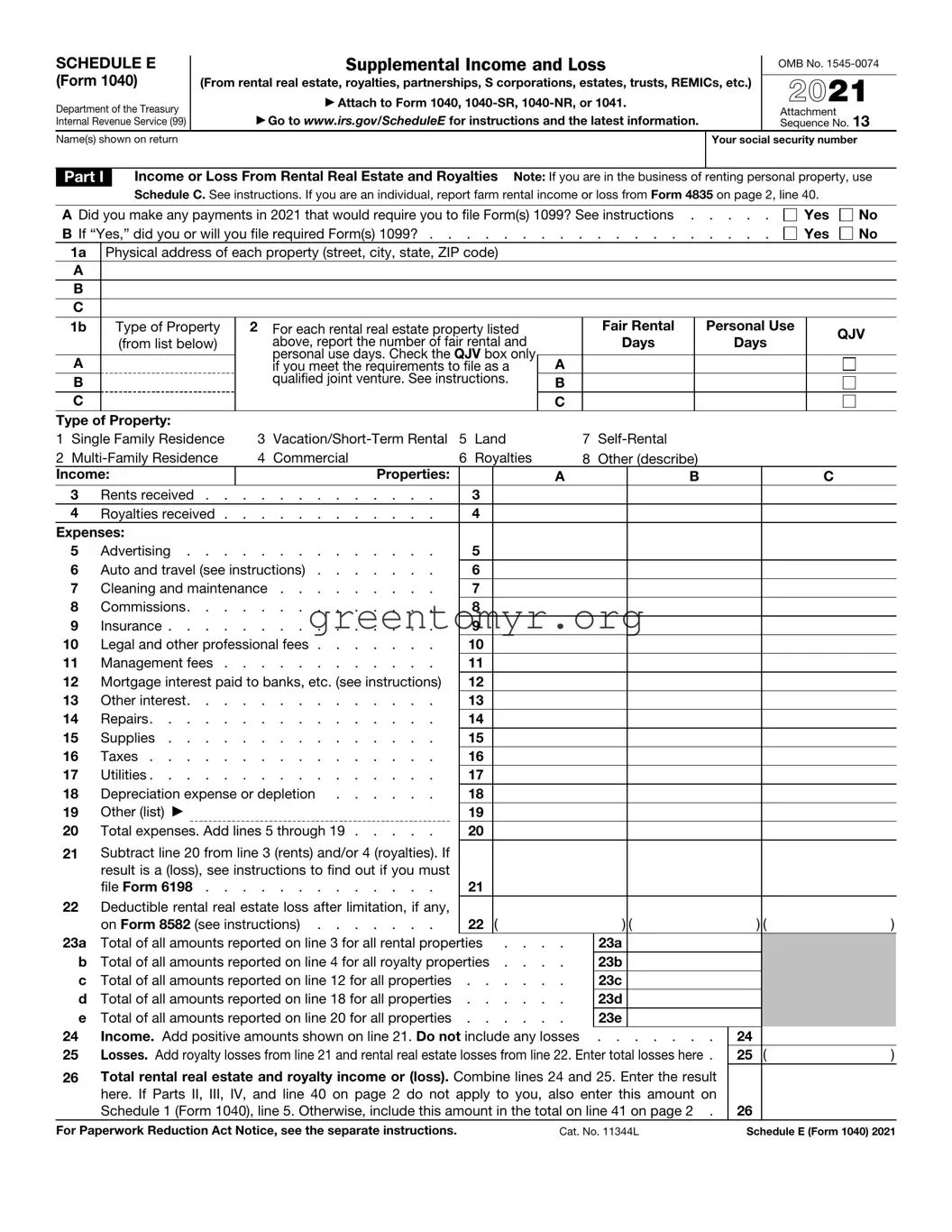
Filling out the IRS Schedule E (Form 1040) can be a daunting task. Many taxpayers stumble upon common mistakes that can lead to trouble down the line. One of the most frequent errors is neglecting to include all sources of rental income. Whether you own multiple properties or just one, ensure that every cent of rental income makes its way onto your Schedule E.
Another common pitfall is failing to accurately report expenses. Many people forget to deduct legitimate expenses, such as property management fees, repairs, or even depreciation. This oversight can lead to paying more taxes than necessary. Every deductible expense counts!
For those who have questions about their ownership status, another mistake arises from inaccurately reporting the ownership type. It’s vital to indicate whether you are a sole proprietor, a partner, or if you have an LLC. Each status comes with its implications for how you report on Schedule E.
Tax filers sometimes miss deadlines, leading to penalties and interest. It’s crucial to submit your Schedule E on time, as part of your overall tax return. Planning ahead and keeping track of deadlines can save headaches in the future.
In addition, omitting the right information about each property is another mistake that can occur. Taxpayers must provide details such as the property address and whether it’s rented out for part of the year or the full year. Incomplete information can raise red flags with the IRS.
Some individuals mistakenly confuse personal use with rental use. If a property is used for personal purposes more than the allowed limit, it may not qualify for full rental-tracking deductions. Knowing how to differentiate personal use from rental use is key to accurate reporting.
Also common is the failure to account for passive activity losses. If you’re subjected to the passive activity loss rules, make sure you understand how to report losses correctly. That way, taxpayers can ensure they’re not missing out on potential tax benefits.
Using inaccurate property values can lead to problems too. It's essential to report market value accurately; an exaggerated value may trigger an audit, while an understated value can lead to lost deductions. Play it safe and base your values on market trends, appraisals, or recent sales data.
Lastly, many overlook the importance of record-keeping. Keeping solid records of all income and expenses is crucial. Without solid documentation, it can be challenging to defend deductions if the IRS comes knocking.
In summary, avoiding these ten common mistakes can make a significant difference. Careful attention to detail when completing the Schedule E form not only streamlines your tax preparation process but also ensures compliance with IRS rules. Staying informed and organized will ultimately lead to a smoother tax experience.