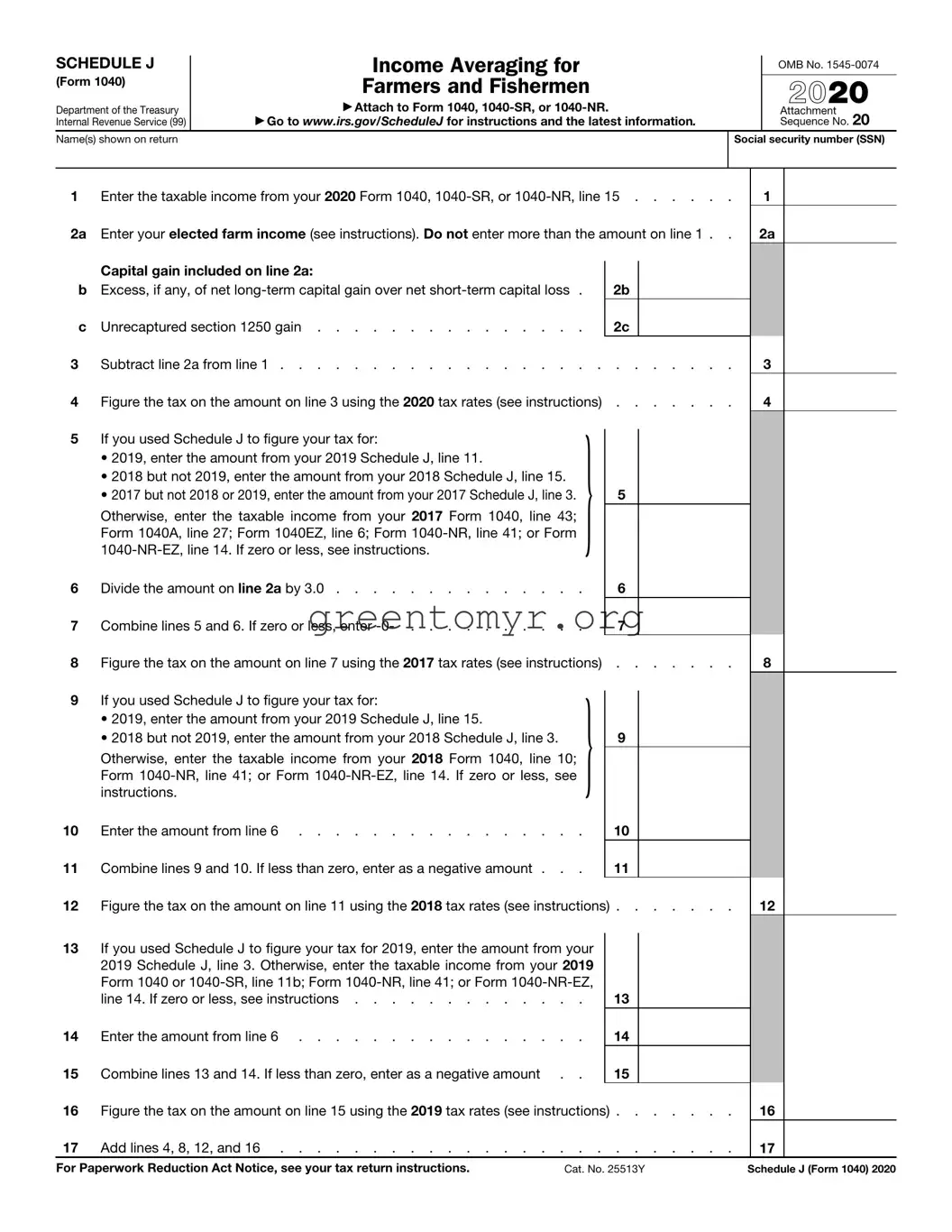
What is IRS Schedule J?
IRS Schedule J is a form used by farmers and fishing industry participants to report income. It allows individuals to average their income over a three-year period, which can help smooth out fluctuations in earnings due to seasonal changes in these industries.
Who should use Schedule J?
Taxpayers engaged in farming or fishing activities, whose income varies from year to year, may benefit from this form. If your gross income from these activities is more than $1,000 and you wish to stabilize your tax liability, filling out Schedule J may be appropriate.
How do I fill out Schedule J?
To fill out Schedule J, you need to gather financial information from the past three years related to your farming or fishing income. The process includes:
-
Calculating your total income for each of the three years.
-
Averaging your income by adding the total amounts together and dividing by three.
-
Completing the form with the averaged amounts and calculating your tax based on this income.
What are the benefits of using Schedule J?
The primary advantage of using Schedule J is the ability to average out income, which can result in a lower tax rate during low-income years. This averaging can also lessen the tax burden during more profitable years, leading to potential tax savings.
Can I use Schedule J if I don't have income from farming or fishing?
No, Schedule J is specifically designed for individuals whose income arises from farming or fishing activities. If you do not earn income from these sources, you should utilize other forms that are applicable to your tax situation.
What happens if I do not file Schedule J?
If you qualify to use Schedule J but choose not to file it, your income will be taxed without the benefit of averaging. This could lead to a higher tax liability, especially in years with significant fluctuations in income. Therefore, it is essential to assess your eligibility for this form to determine the best tax strategy.
Where can I find Schedule J and instructions for filing?
Schedule J and its accompanying instructions can be found on the IRS website. The forms are available for download, and you can also find detailed guidance on how to complete the form correctly. It's advisable to carefully review the instructions to ensure compliance with all requirements.